¡Monoclonal antibodies are everywhere now – Part 3!
Simple, that’s how they are made
September 30 2024
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) originate from a single parent cell, so they bind exclusively to a single epitope (an epitope, or antigenic determinant, is a part of a molecule that will be recognized by an antibody and to which it will bind).
There are several strategies for generating therapeutic mAbs. Two of the most common production methods are hybridoma production and phage display.
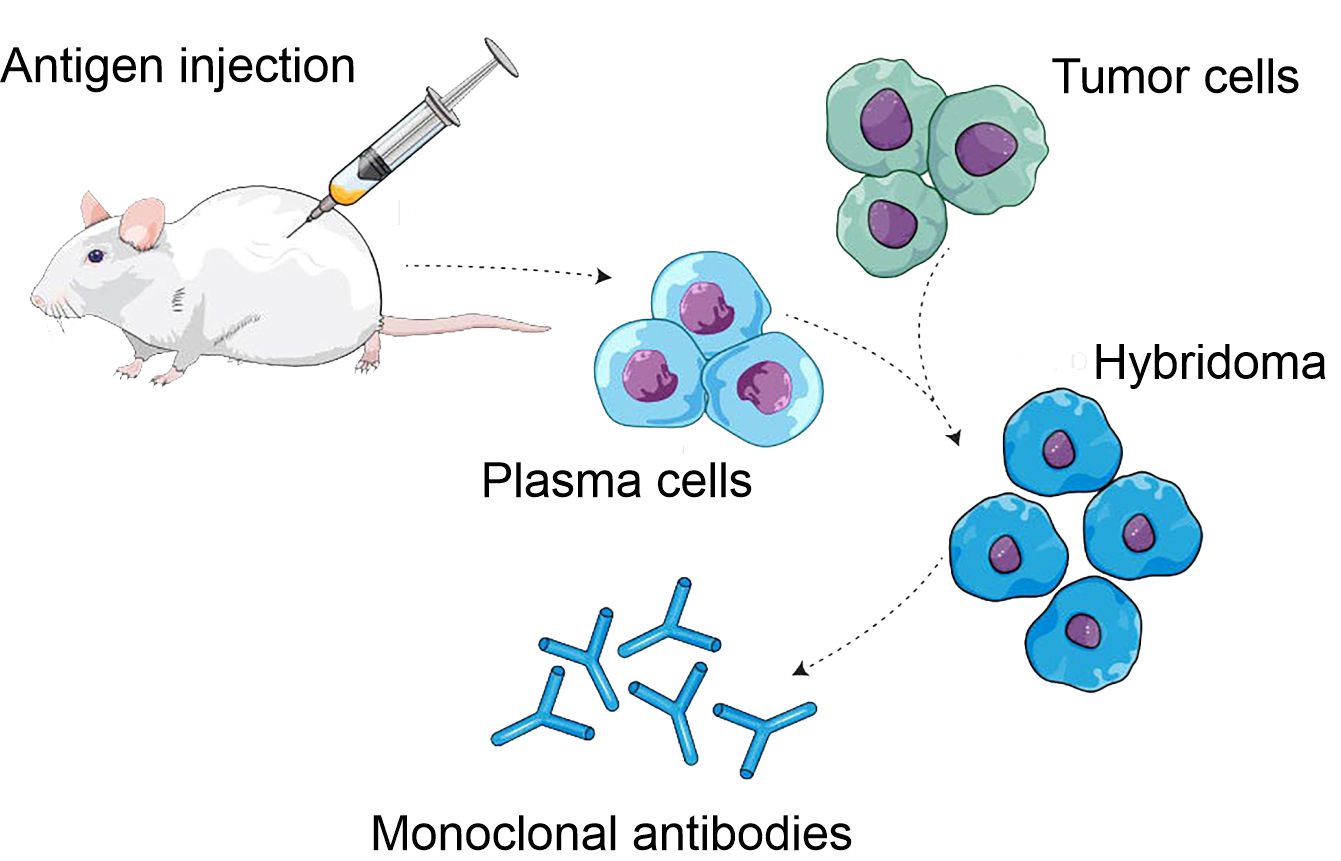
Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large quantities of identical antibodies, so-called monoclonal antibodies.
¿How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
The traditional mAb production process typically begins with the generation of mAb-producing cells (i.e., hybridomas) by fusing myeloma cells with the desired antibody-producing splenocytes (a splenocyte is a white blood cell residing in the spleen) (i.e., B cells). These B cells are generally derived from animals, usually mice. Following cell fusion, large numbers of clones are screened and selected based on antigen specificity and immunoglobulin class. Once candidate hybridoma cell lines are identified, each “hit” is confirmed. Upon completion, the clones are scaled up where additional downstream bioprocesses occur.
¿And so, how many types of monoclonal antibodies are made?……
