¡Monoclonal antibodies, yes, and there are also polyclonal antibodies –
Part 7!
Polyclonals have many applications
We know well that there are many types of monoclonal antibodies, and that each monoclonal antibody is produced to bind to a specific, unique antigen. They are used for the diagnosis and treatment of many diseases, including some types of cancer. They can be useful alone, or combined with other compounds, to carry drugs, toxins, or radioactive substances directly to specific cells.

pAbs have a wide range of applications, including diagnostic tests as well as biological analyses. For example, in immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry techniques, such as ELISA, to detect tumor markers and other proteins of interest.
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs), such as Rho(D) immunoglobulin, are injected into Rhesus-negative mothers to prevent hemolytic disease in the newborn.
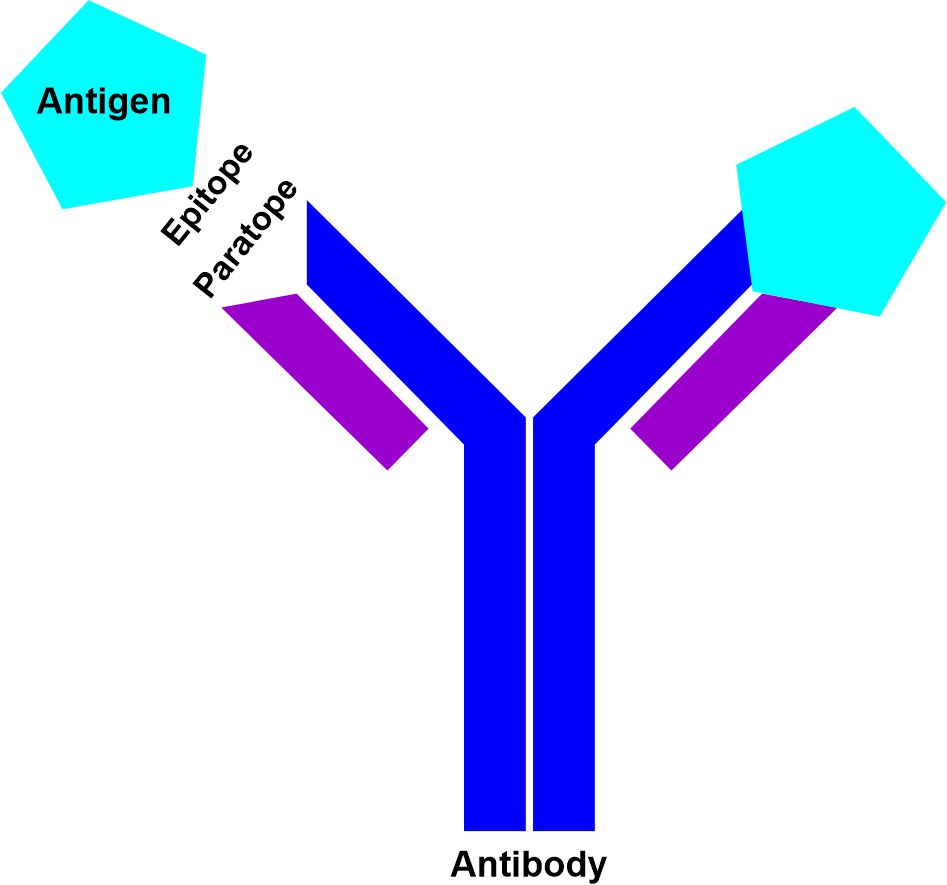
Another advantage is that they have greater affinity against the antigen, due to the recognition of multiple epitopes, and they have a high sensitivity to detect proteins that are found in low quantities.
Finally, because they are more stable, they are easier to store.
We will continue this series, briefly talking about recombinant monoclonal antibodies……
